Short for Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, ARPANET or ARPAnet began development in 1966 by the United States ARPA. ARPANET was a Wide Area Network linking many Universities and research centers, was first to use packet switching, and was the beginning of what we consider the Internet today. Some of the reasons for creating ARPANET include making it easier for people to access computers, to improve computer equipment, and to have a more effective communication method for the military.
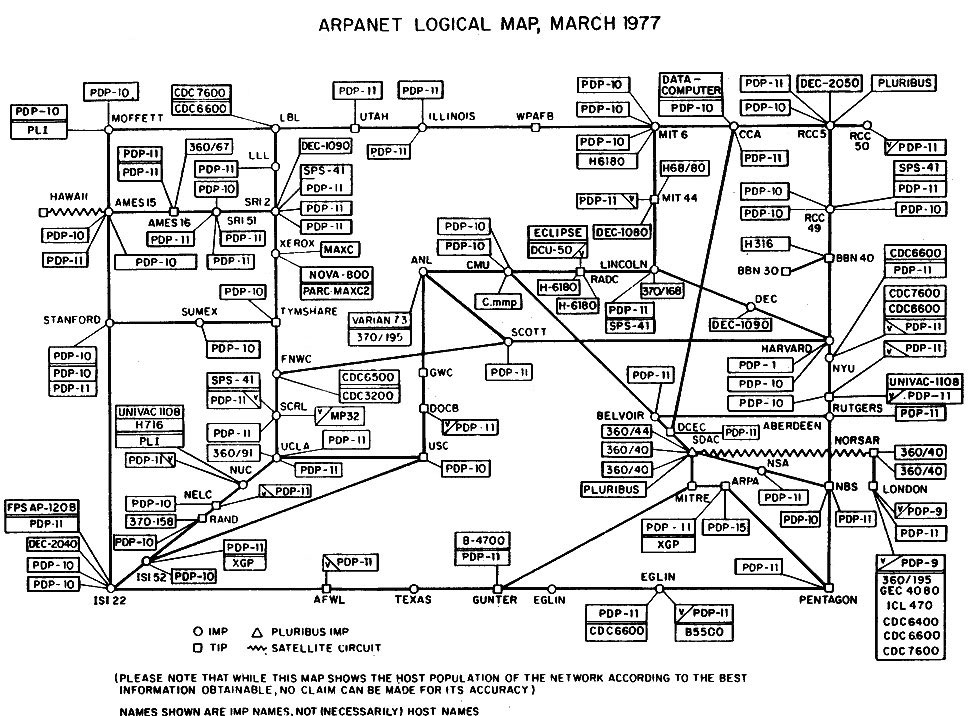
ARPANET first came into existence when the first two nodes were established between UCLA and Stanford Research Institute (SRI) in 1969 followed shortly thereafter by UCSB and the University of Utah. In the picture below is an example of what ARPANET looked like in March 1977, click the image to see a larger view of the image.
ARPANET completed its transition to TCP/IP on January 2, 1983, was later replaced by NSFNET in 1990, and then decommissioned on February 28, 1990.
0 comments:
Post a Comment